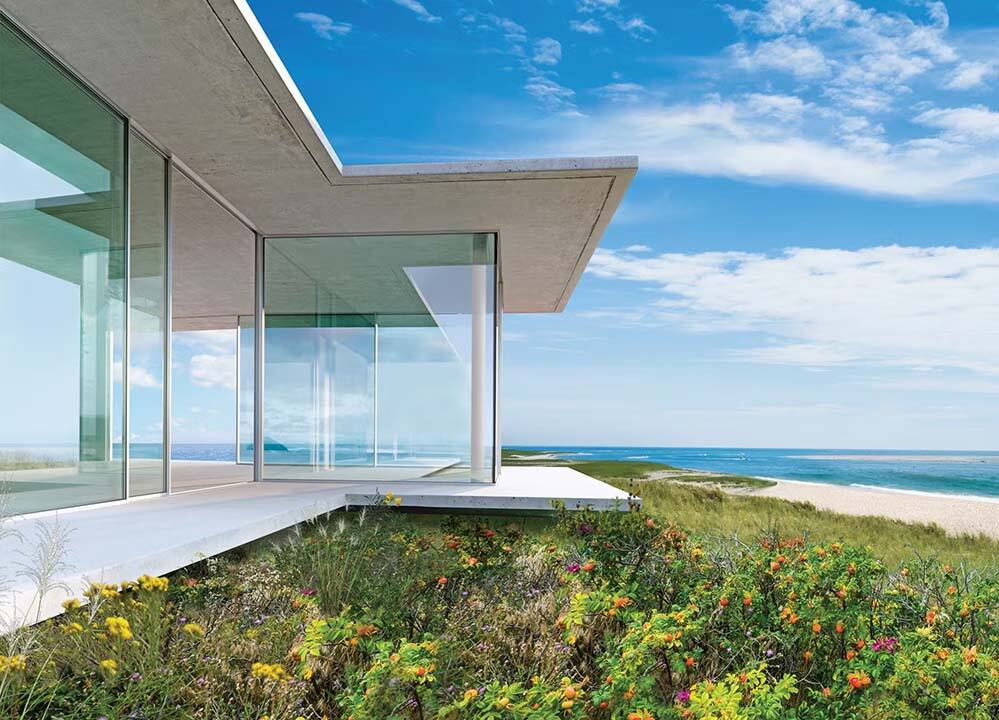
What Is The Role Of Low-E Glass In Doors And Windows?
Good windows always come with good glass. Low-E means low emissivity (low-e or low thermal emissivity) is a surface condition that emits low levels of radiant thermal (thermal) energy.Coating it on a glass surface reduces the emissivity from below 0.84 to 0.15. How does LOW-E glass exert amazing effects? Let’s discuss:
Features of Low-E Glass
- Thermal Insulation: By adding a metal film on the surface of the glass, it effectively blocks the transmission of heat, reduces the exchange of indoor and outdoor temperatures, provides better thermal insulation effects, and reduces energy consumption for heating and air conditioning.
- Energy saving and environmental protection: Reduce heat loss, improve the energy utilization efficiency of the building, reduce energy consumption, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and being more environmentally friendly.
- The shading coefficient SC is wide and the amount of sunlight penetration can be controlled as needed to adapt to different needs.
- UV protection: LOW-E glass can filter out ultraviolet radiation, reduce the damage of ultraviolet rays to skin and indoor items, and extend the service life of items.

How does Low-E Glass work in summer and winter?
In winter, the indoor temperature is higher than the outdoor temperature, and infrared heat mainly comes from indoors. Low-E glass can reflect the heat back into the room, thereby keeping indoor heat from leaking. For outdoor solar radiation, Low-E glass will still let it in. This energy will be absorbed by indoor objects and then converted into infrared heat and retained indoors.
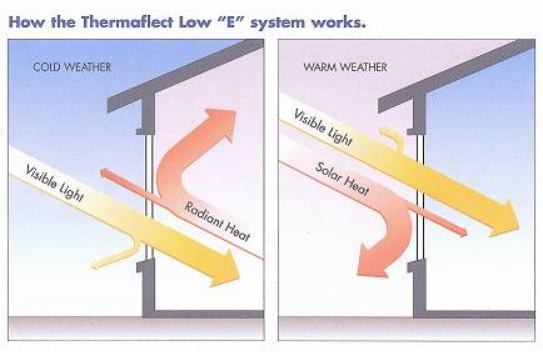
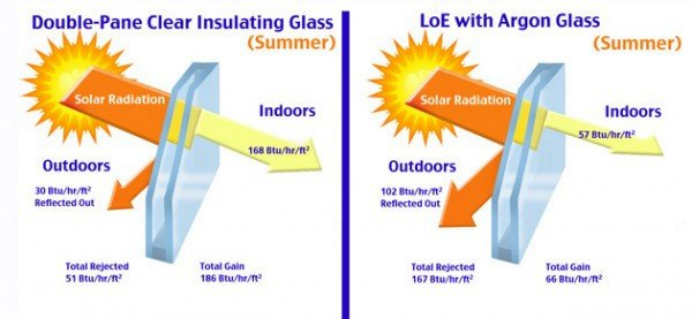
In summer, when the outdoor temperature is higher than indoors, infrared heat mainly comes from the outside. Low-E glass can reflect it out, thus preventing heat from flowing into the room. For outdoor solar radiation, Low-E glass limits its penetration indoors, thus reducing energy costs (such as air conditioning bills)
Argon in Vacuum Low-E Glass
- Filling with argon can reduce the internal and external pressure difference, maintain pressure balance, and reduce glass bursts caused by pressure differences.
- After filling with argon, the K value of the insulating glass can be effectively improved, reducing condensation on the indoor side glass, and improving the comfort level. That is, the inflated insulating glass is less likely to condensation and frost, but not inflating does not cause dew and frost. The direct cause of fog.
- Due to the characteristics of argon as an inert gas, it can slow down the heat convection in the insulating glass, and at the same time, it can also greatly improve its sound insulation and noise reduction effect, that is, it can make the insulation and sound insulation effect of the insulating glass better. .
- It can increase the strength of large-area insulating glass so that the middle will not collapse due to lack of support.
- Increase wind pressure resistance.
- Because it is filled with dry inert gas, the air containing moisture in the hollow cavity can be replaced, keeping the environment in the cavity drier and extending the service life of the molecular sieve in the aluminum spacer frame.
- When using low-emissivity LOW-E glass or coated glass, since the filled gas is an inactive inert gas, it can protect the film layer, reduce the oxidation rate, and extend the service life of the coated glass.
Low-E has significant effects on the attenuation of UV
Low-E glass reduces UV rays by 25% compared to single-layer clear glass.Compared with heat-reflective coated glass, Low-E glass can reduce UV rays by 14%.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 HY
HY
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 GU
GU
 TA
TA